The Importance of Encryption in Securing Your Digital Life
"Protecting Your Personal Information in the Age of Cyber Threats"
Introduction
The plain text must be encrypted to make it unreadable without a decryption key. It is an essential part of digital security, fending off threats to digitally stored personal and financial information. In the age of technology, encryption is more important than ever because we disclose so many of our private matters online.
Why Encryption is Important?
Encryption safeguards your personal and financial data against illegal access. Personal information includes things like your name, address, social security number, and medical data. Bank account numbers, credit card details, and tax data are examples of financial information. Encryption also safeguards your communications, including email and instant messaging.

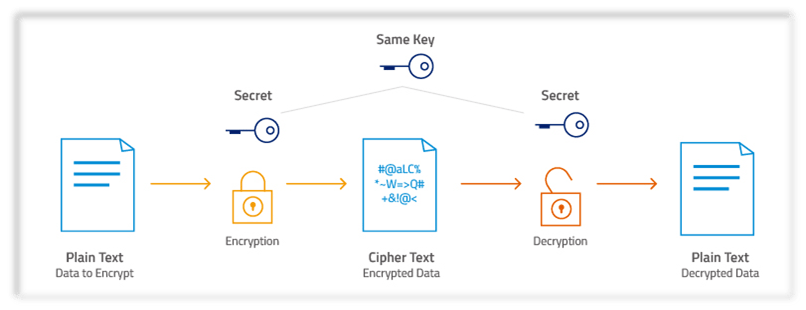
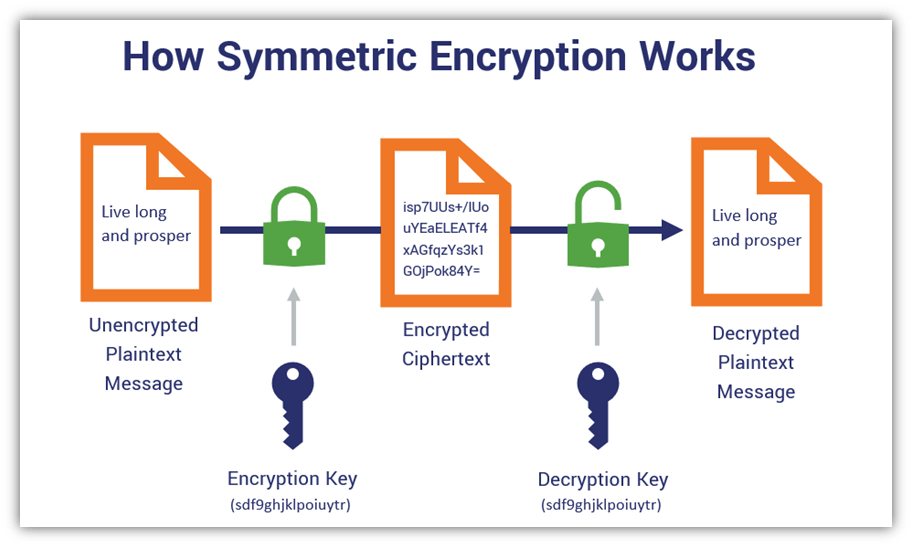
How Encryption Works
Encryption works by converting plain text into code that is unintelligible without a decryption key using complicated algorithms. There are two kinds of encryption: symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption. Asymmetric encryption employs distinct keys for each procedure, whereas symmetric encryption uses the same key for both encryption and decryption.
Encryption in Everyday Life
Encryption is necessary for many parts of our daily lives, including online banking, messaging services, and cloud storage. The data you submit while logging into your online banking account is encrypted before being sent to the bank's server. Encryption is used by messaging services like Facebook and Signal to prevent message eavesdropping. Cloud storage providers like Google Drive and Dropbox safeguard your files against illegal access. You can use internet services without fear of your data being hacked since encryption helps keep your data private and secure. It is a crucial element of contemporary digital life.

Challenges with Encryption
Encryption has its challenges, despite its importance. It might be challenging for non-technical individuals to efficiently apply encryption due to accessibility and usability difficulties. Criminals can also use encryption to cover up illicit activity. Moreover, encryption can be used to get around restrictions and monitoring, which is a double-edged sword because it can be applied to both positive and negative ends. Governments and businesses must exercise caution while regulating encryption to avoid impeding its advantages. It may be necessary for government organisations to have access to encrypted data in order to protect national security. For example, in the UK, the Investigatory Powers Act 2016 gives law enforcement and intelligence services the power to order companies to provide access to communications, including encrypted messages.

Conclusion
We need encryption to protect our financial and personal information in today's digital age. While encryption has its challenges, the benefits far outweigh the risks. Encryption adds, on average, 15% latency. By using encryption in everyday life, we can protect ourselves from cyber threats and safeguard our privacy. Nevertheless, the added protection of encryption is worth the additional latency, as it can greatly reduce the risk of a data breach or unauthorised access to our confidential information.
FAQ's
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is a technology that allows users to access and manage data and applications over the internet. For instance, a business could use cloud computing to store customer data and manage their accounting software online. instead of storing them locally on their devices. As a result, it involves providing computing services such as servers, storage, databases, networks, software, and analytics via the Internet. For instance, Google Drive is a cloud computing service that allows users to store their documents in the cloud and access them from anywhere.
What are the benefits of using cloud computing?
Cloud computing offers several benefits, including:
Cost savings: By removing the need for enterprises to buy and maintain pricey gear and software, cloud computing lowers overall expenses.
Scalability: Depending on their demands, organisations can rapidly and effectively scale their computing resources up or down using cloud computing.
Flexibility: With cloud computing, workers may use any device to access data and applications at any time and from any location.
Security: To safeguard data from online dangers, cloud computing providers offer cutting-edge security features and procedures.
Data recovery: In the event of a disaster, such as a power outage or system failure, services are provided via cloud computing. Scalability: Users can scale up or down cloud computing services according to their demands, which saves them time and money. Cost-effectiveness: Cloud computing services are affordable and can drastically lower IT costs.
What are some examples of cloud computing services?
There are several examples of cloud computing services, including:
SaaS (software as a service) examples include Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, and Salesforce. SaaS solutions often provide online access to software programmes and services on a subscription basis. They can be accessed from any device with an internet connection and are frequently housed in the cloud.
Examples of cloud storage include Google Drive, Dropbox, and ICloud. So instead storing their files, data, and documents locally on their computer, users can do so remotely using cloud storage services. Any internet-connected device can access files stored in cloud storage.
Is cloud computing secure?
Computing in the cloud can be secure, but it depends on the precautions the user and cloud service provider take. To safeguard data from cyberattacks, cloud computing services often use advanced security features, including encryption, firewalls, and access controls. To maintain cloud data security, users must also take safeguards, including using strong passwords, upgrading software often, and implementing two-factor authentication.
